Plots
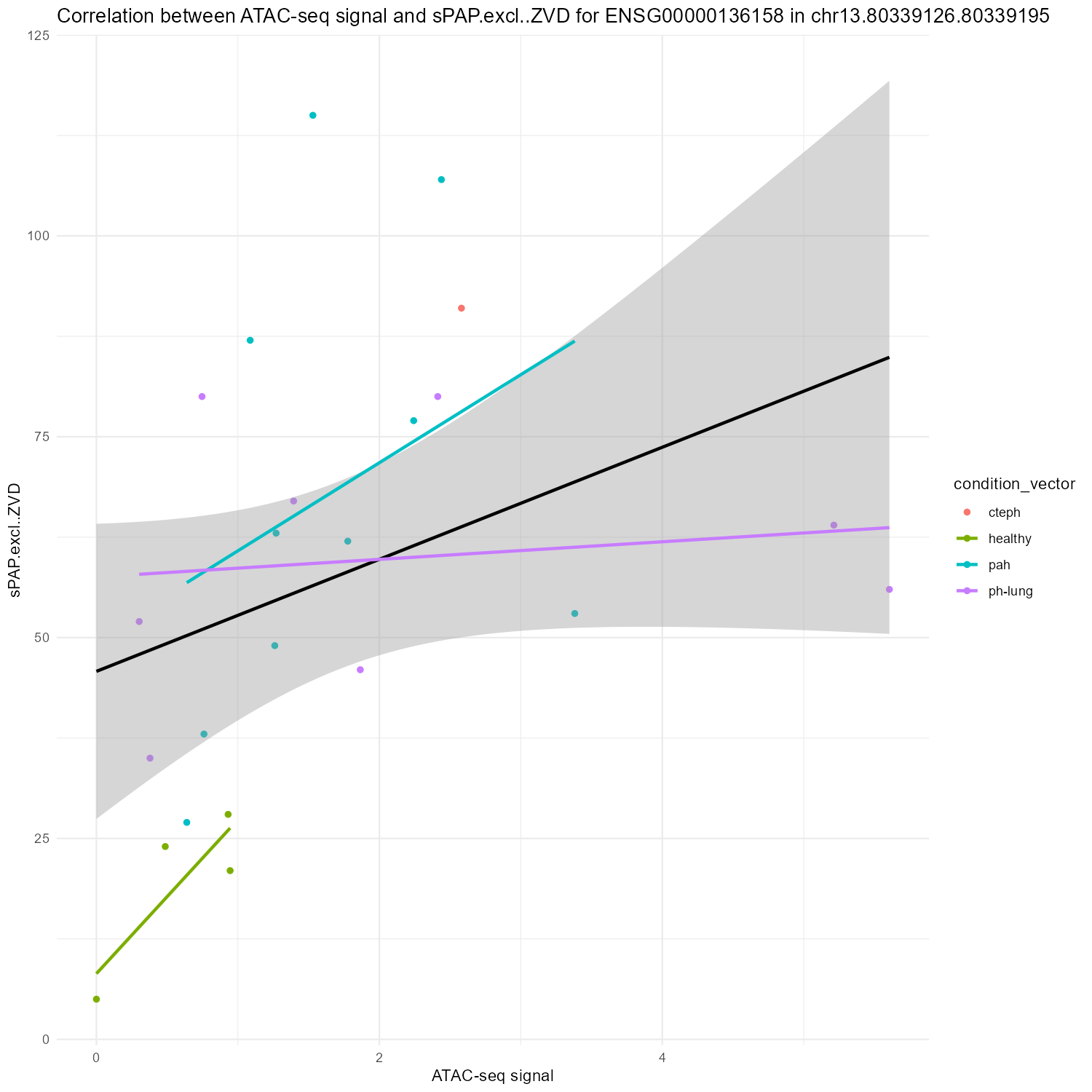
sPAP
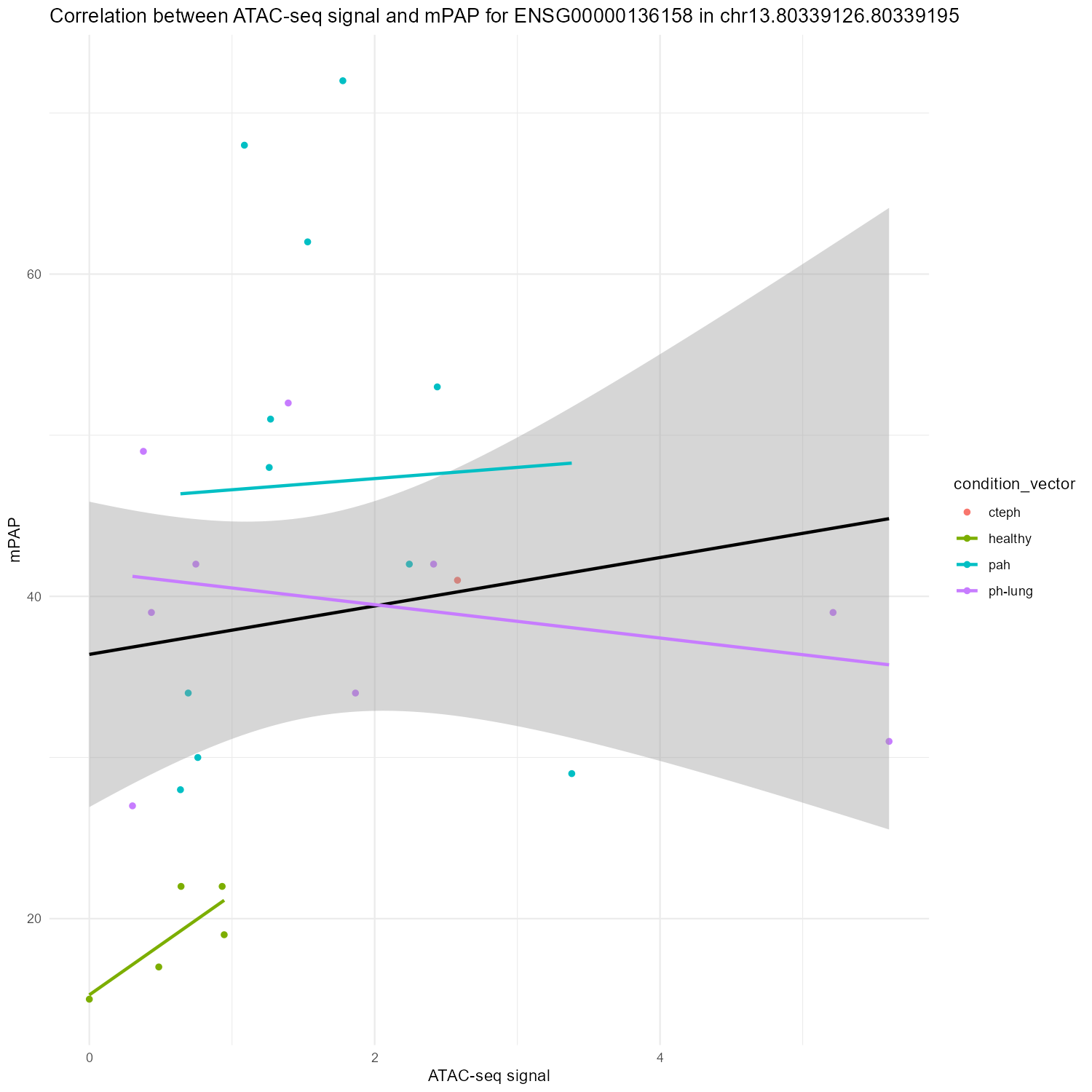
mPAP
Info
NCBI Gene Summary for SPRY2 Gene
- This gene encodes a protein belonging to the sprouty family. The encoded protein contains a carboxyl-terminal cysteine-rich domain essential for the inhibitory activity on receptor tyrosine kinase signaling proteins and is required for growth factor stimulated translocation of the protein to membrane ruffles. In primary dermal endothelial cells this gene is transiently upregulated in response to fibroblast growth factor two. This protein is indirectly involved in the non-cell autonomous inhibitory effect on fibroblast growth factor two signaling. The protein interacts with Cas-Br-M (murine) ectropic retroviral transforming sequence, and can function as a bimodal regulator of epidermal growth factor receptor/mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling. This protein may play a role in alveoli branching during lung development as shown by a similar mouse protein. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]
GeneCards Summary for SPRY2 Gene
SPRY2 (Sprouty RTK Signaling Antagonist 2) is a Protein Coding gene. Diseases associated with SPRY2 include Iga Nephropathy 3 and Adrenal Cortical Adenocarcinoma. Among its related pathways are Negative regulation of FGFR3 signaling and Signaling by FGFR2. Gene Ontology (GO) annotations related to this gene include protein kinase binding and protein serine/threonine kinase inhibitor activity. An important paralog of this gene is SPRY1.
Consensus
Receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) have been implicated in the pathogenesis of PH through their role in promoting the proliferation and survival of pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells (PASMCs). RTKs play a crucial role in the pathogenesis of pulmonary hypertension by promoting PASMC proliferation and survival. Targeting the PI3K p110α subunit, a key downstream effector of RTK signaling, shows promise in preventing and reversing PH.